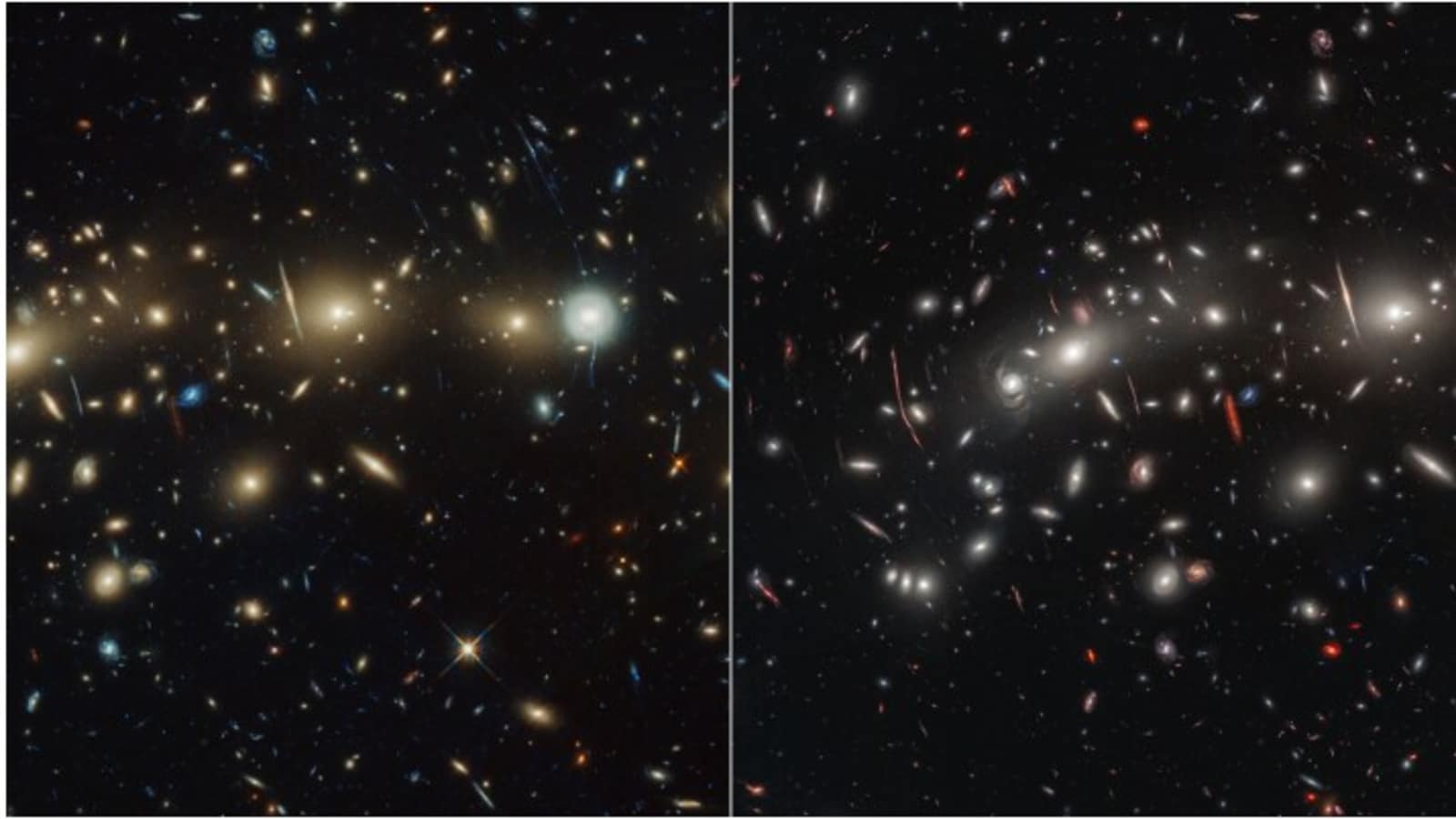
In an extraordinary cosmic collaboration, NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope and the Hubble Space Telescope have partnered to explore the vastness of a distant galaxy cluster and they have unveiled a mesmerising and vibrant panorama of the universe. This groundbreaking venture, capturing the galaxy cluster known as MACS0416, employs a fusion of visible and infrared light, producing one of the most extensive snapshots of the universe to date.
MACS0416’s Dance of Galaxies
Situated a staggering 4.3 billion light-years away from Earth, MACS0416 comprises two colliding galaxy clusters destined to merge into an even grander cosmic entity. The composite image not only showcases a multitude of galaxies beyond the cluster but also unveils dynamic sources, likely influenced by gravitational lensing- a phenomenon altering and intensifying light from distant celestial sources.
We are now on WhatsApp. Click to join.
This celestial cluster marks the inaugural subject of a revolutionary Hubble initiative, the Frontier Fields program, initiated in 2014, aiming to deliver unprecedented, super-deep insights into the universe.
James Webb Telescope’s Cosmic Revelation
Hubble Telescope, a pioneer in detecting faint and youthful galaxies, sees its capabilities expanded by the James Webb Space Telescope’s infrared perspective, delving deeper into the cosmic dawn. The research team, incorporating three observation epochs from both telescopes, alongside a fourth from the CANUCS research team, identified 14 transients—objects exhibiting varying brightness over time.
Twelve of these phenomena were pinpointed in highly magnified galaxies due to gravitational lensing, likely representing momentarily intensified individual stars or multi-star systems. The remaining two transients, residing in moderately magnified background galaxies, are suspected supernovae.
A standout discovery among these transients is “Mothra,” located in a galaxy that emerged approximately 3 billion years post-Big Bang. Magnified by a factor exceeding 4,000, Mothra earned its moniker due to its extraordinary luminosity and magnification. Intriguingly, Hubble observations from nine years prior also captured Mothra, hinting at an additional object within the foreground cluster intensifying the magnification. While the team determined Mothra’s mass to range between 10,000 and 1 million times that of our Sun, the identity of this enigmatic “milli-lens” remains elusive.
Beyond the visual spectacle, this collaboration between James Webb Space Telescope and Hubble Space Telescope significantly advances our comprehension of galaxy formation and evolution. The revelation of numerous transients suggests that continual monitoring with James Webb Space Telescope may unveil a multitude of similar phenomena within this and similar clusters, adding yet more layers to our understanding of the cosmic tapestry.
One more thing! HT Tech is now on WhatsApp Channels! Follow us by clicking the link so you never miss any updates from the world of technology. Click here to join now!

Shambhu Kumar is a science communicator, making complex scientific topics accessible to all. His articles explore breakthroughs in various scientific disciplines, from space exploration to cutting-edge research.