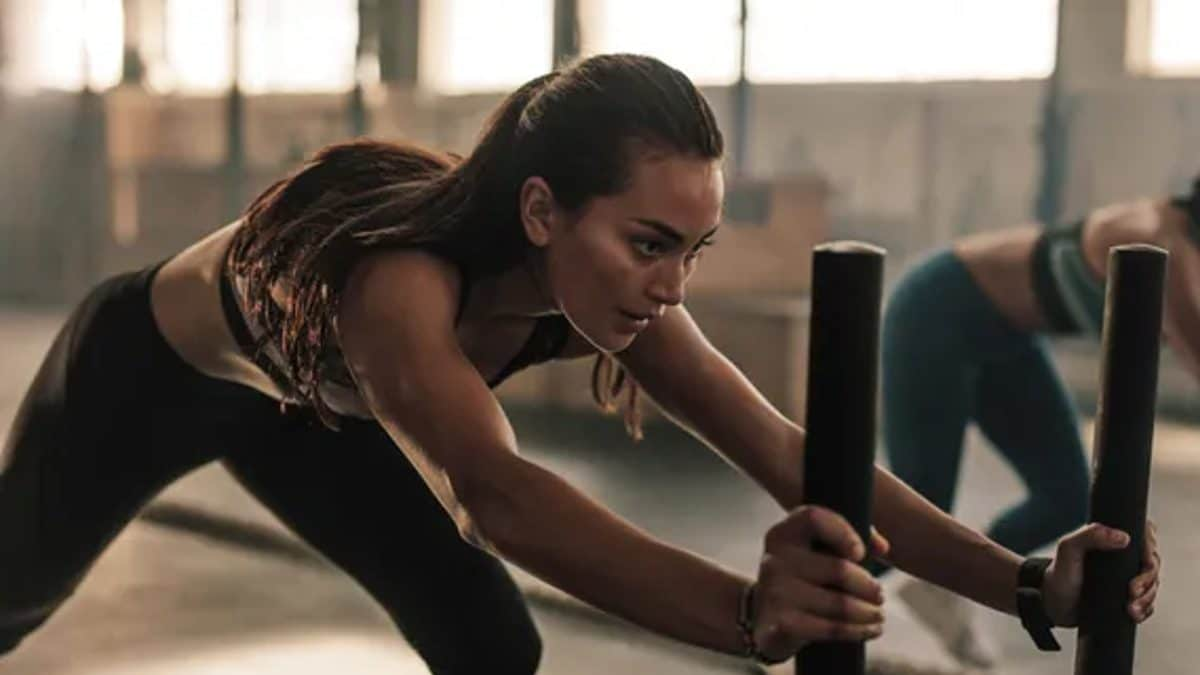Exercise that is strenuous enough to temporarily disturb the heart’s electrical system can cause arrhythmias, which are irregular heartbeats.
By Dr Santosh Kumar Dora, Senior Cardiologist, Asian Heart Institute, Mumbai details bout the risks of intense exercises, balancing the intensity, heart health and everything else that is related.
Regular physical activity is widely acknowledged as a cornerstone of a healthy lifestyle, promoting cardiovascular fitness, mental well-being, and longevity. While moderate exercise remains beneficial, it is crucial to be aware of the potential drawbacks associated with extreme exercise to make informed choices and prioritize heart health.
When the body is pushed beyond its limits without adequate rest and recovery, it can lead to an increased risk of developing cardiovascular conditions, such as myocardial damage, and cardiac arrhythmias (Although exercise, when performed in moderation, is known to reduce the risk of heart rhythm abnormalities, prolonged and excessive high-intensity workouts may have the opposite effect), and increased susceptibility to infections. One potential risk associated with intense exercise is an overtraining syndrome (when an individual exceeds their body’s ability to recover from the stress of exercise, leading to a state of chronic fatigue and impaired performance).
Vigorous exercise can temporarily disrupt the heart’s electrical system, resulting in abnormal heartbeats or arrhythmias. While these episodes are often benign and self-limiting, they can occasionally lead to more serious conditions, such as atrial fibrillation or ventricular tachycardia. Individuals with a history of heart disease or arrhythmias should consult with their healthcare provider to establish safe exercise parameters and mitigate potential risks.
To protect your heart while reaping the benefits of exercise, it is crucial to adopt safe exercise practices. Here are some recommendations to consider:
- Increase exercise intensity gradually:
Avoid abrupt and drastic increases in exercise intensity. Instead, gradually progress your workouts to allow your body to adapt and minimize the risk of overexertion. - Listen to your body:
Pay attention to signs of overtraining, such as persistent fatigue, decreased performance, or an elevated resting heart rate. If you experience these symptoms, take a break, and allow yourself ample time to recover. - Incorporate rest days:
Allow your body sufficient time to recover between intense workouts. Adequate rest is vital for muscle repair, hormone balance, and overall cardiovascular health. - Maintain a balanced exercise routine:
Include a variety of exercises in your routine, combining cardiovascular activities with strength training, flexibility exercises, and low-impact workouts to reduce the strain on your heart and joints. - Stay hydrated:
Proper hydration is essential for optimal cardiovascular function. Drink water before, during, and after exercise to maintain adequate fluid balance. - Stay mindful of warning signs:
If you experience chest pain, palpitations, severe shortness of breath, or dizziness during or after exercise, seek medical attention promptly.
While intense exercise is often touted for its health benefits, it is crucial to be aware of the potential risks it poses to the heart. It is also advised to seek guidance from a qualified healthcare provider before starting or modifying an exercise program.

Exercise that is strenuous enough to temporarily disturb the heart’s electrical system can cause arrhythmias, which are irregular heartbeats.
Understanding the Risks of Intense Exercise for Heart Health
Regular physical activity is widely recognized as essential for maintaining a healthy lifestyle. It not only promotes cardiovascular fitness and mental well-being but also contributes to longevity. While moderate exercise is generally beneficial, it is important to be aware of the potential drawbacks associated with extreme exercise and make informed choices that prioritize heart health.
Pushing your body beyond its limits without adequate rest and recovery can increase the risk of developing cardiovascular conditions such as myocardial damage and cardiac arrhythmias. Although moderate exercise is known to reduce the risk of heart rhythm abnormalities, prolonged and excessive high-intensity workouts may have the opposite effect. Additionally, intense exercise can weaken the immune system, making you more susceptible to infections. Overtraining syndrome is another potential risk, resulting in chronic fatigue and impaired performance when the body cannot properly recover from exercise-induced stress.
Intense exercise can temporarily disrupt the heart’s electrical system, leading to abnormal heartbeats or arrhythmias. While these episodes are often harmless and resolve on their own, they can occasionally progress to more serious conditions like atrial fibrillation or ventricular tachycardia. Individuals with a history of heart disease or arrhythmias should consult with their healthcare provider to establish safe exercise parameters and mitigate potential risks.
To protect your heart while maximizing the benefits of exercise, it is crucial to follow safe exercise practices. Here are some recommendations:
- Increase exercise intensity gradually:
Avoid sudden and drastic increases in exercise intensity. Instead, gradually progress your workouts to allow your body to adapt and minimize the risk of overexertion. - Listen to your body:
Pay attention to signs of overtraining, such as persistent fatigue, decreased performance, or an elevated resting heart rate. If you experience these symptoms, take a break and allow yourself ample time to recover. - Incorporate rest days:
Give your body sufficient time to recover between intense workouts. Adequate rest is crucial for muscle repair, hormone balance, and overall cardiovascular health. - Maintain a balanced exercise routine:
Include a variety of exercises in your routine, combining cardiovascular activities with strength training, flexibility exercises, and low-impact workouts to reduce strain on your heart and joints. - Stay hydrated:
Proper hydration is essential for optimal cardiovascular function. Drink water before, during, and after exercise to maintain adequate fluid balance. - Stay mindful of warning signs:
If you experience chest pain, palpitations, severe shortness of breath, or dizziness during or after exercise, seek medical attention promptly.
Denial of responsibility! SamacharCentrl is an automatic aggregator of Global media. In each content, the hyperlink to the primary source is specified. All trademarks belong to their rightful owners, and all materials to their authors. For any complaint, please reach us at – [email protected]. We will take necessary action within 24 hours.

Hemalata Nehete celebrates the art of living well, exploring topics ranging from travel and fashion to home decor and culinary delights, offering inspiration for readers seeking a balanced and enjoyable lifestyle.
Denial of responsibility! Samachar Central is an automatic aggregator of Global media. In each content, the hyperlink to the primary source is specified. All trademarks belong to their rightful owners, and all materials to their authors. For any complaint, please reach us at – [email protected]. We will take necessary action within 24 hours.