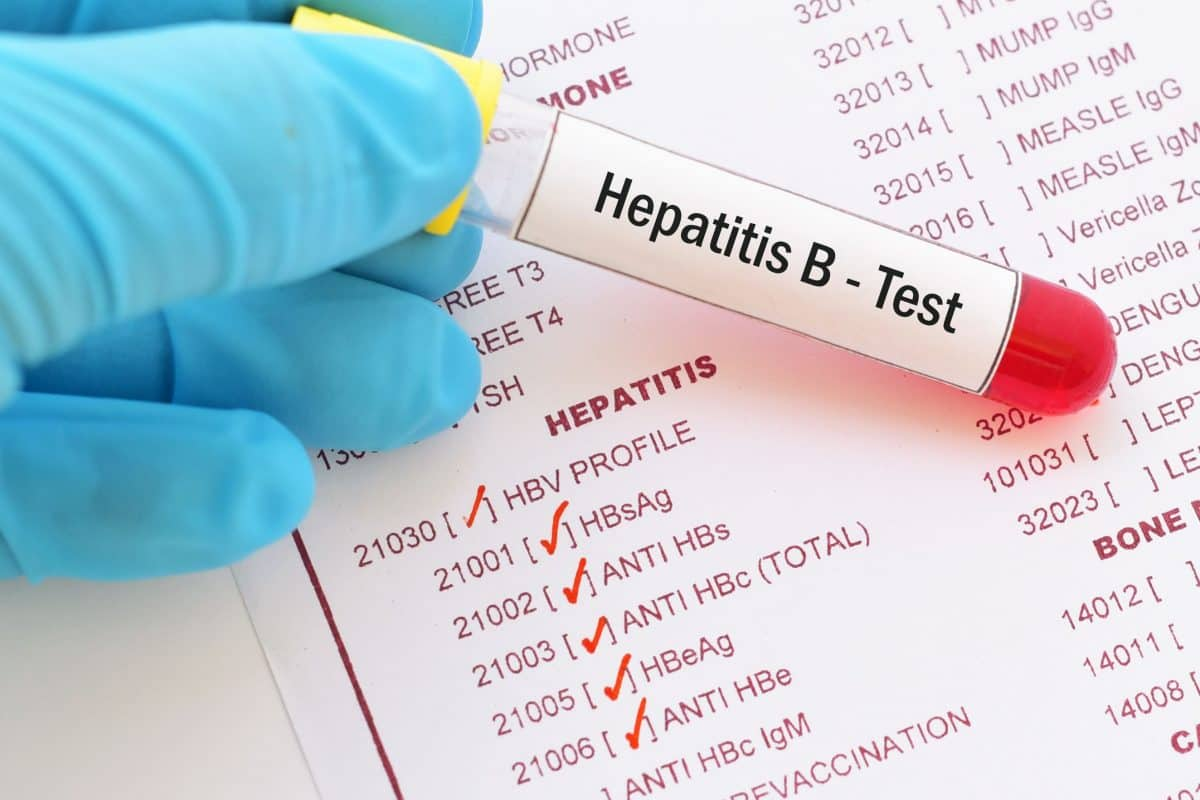
The primary reason to screen for Hepatitis B and C infection is to reduce morbidity and mortality associated with chronic liver disease and to curtail transmission.
World Liver Day 2024: Hepatitis B and C attack the liver, causing acute and chronic liver disease. The hepatitis B and C viruses are bloodborne pathogens, with most infections occurring due to exposure to needle stick injuries, unscreened blood transfusions, drug injections, and unprotected sex. Additionally, hepatitis B and C can spread from mother to child during birth (perinatal transmission) or through horizontal transmission, such as exposure to infected blood. Chronic infection is joint among infants who acquire the infection from their mothers.
According To The World Health Organization (WHO) 2022
A staggering 254 million people suffer from chronic Hepatitis B, with an additional 58 million affected by HCV infection. The vaccine can prevent hepatitis B, whereas Hepatitis C has no effective vaccine. Many prospective and retrospective cohort studies have shown that many individuals are unaware of their Hepatitis infection status and did not receive any therapy. Furthermore, people unaware of their infection status may unknowingly transmit the virus to unprotected individuals.
Screening Benefits, Guidelines And Recommendations
All guidelines recommend screening for Hepatitis B and C infection among populations with a high prevalence of chronic hepatitis, individuals at high risk of acquiring infection, such as dialysis patients, and those requiring repeated blood transfusions.
- Hepatitis B and C in individuals who inject drugs, homosexuals, persons with altered liver enzymes, and people receiving immunosuppressive therapy for various reasons.
- Hepatitis screening is mandatory for all pregnant women, infants born to HBsAg-positive mothers, HIV-positive patients, persons exposed to needle stick injury, and donors of blood and plasma. Many of them who are infected with Hepatitis virus may not have any symptoms when newly infected.
- The patient might take some while to display signs. This is called the incubation period. It may range between 30 days and 180 days for the Hepatitis B virus and two weeks to six months for the Hepatitis C virus.
- Some may develop an acute illness with symptoms that last for several weeks, like yellowing of the skin and eyes, known as jaundice, dark yell-urine, pale-coloured motion, fatigue, nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain.
Treatment Advances
Chronic infection with both Hepatitis B and C can lead to fatal liver cirrhosis and Hepatocellular carcinoma. The primary reason to screen for Hepatitis B and C infection is to reduce morbidity and mortality associated with chronic liver disease and to curtail transmission.
(This article has been verified by Dr R Lakshmipriya, Senior Consultant Microbiologist and Molecular Biologist, Metropolis Healthcare Limited)

Rohit Malhotra is a medical expert and health journalist who offers evidence-based advice on fitness, nutrition, and mental well-being. His articles aim to help readers lead healthier lives.